Subluxation
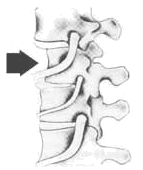
The term subluxation means minor misalignment of a vertebrae. However, the effects on the human body as a result of a subluxation on the upper cervical spine for example, can be far from minor. In the simplest of terms, a subluxation is when one or more vertebrae (bones in your spine) move out of line and create pressure on spinal nerves, facet joints, recurrent meningeal nerves or discs. Spinal nerves are the nerves that come out from the vertebrae in your spine. Pressure on the nerves or other structures, can cause interference with the signals traveling through them - leading to numerous health related problem.
PATHOMECHANICS, also Subluxation is another term many chiropractors uses to describe the misalignment of a vertebrae. Pathomechanics, thus refers to a "pathology of the mechanics" of the spinal column and for some DCs, is a better term to describe this phenomenon.
Chiropractors commonly recognize five categories of components present in the Vertebral Subluxation Complex (VSC) or, the Pathomechanics of the human spine:
- Spinal Kinesiopathology - is where the bones of the spine become stuck, don't move enough, or move too much.
- Neuropathophysiology (abnormal nervous system function) - nerves can become overexcited and hyperactive. Due to the way the spine is engineered, abnormal spinal function can irritate, pinch, rub or choke the delicate tissue of the spinal cord and nerve roots.
- Myopathology (Abnormal Muscle Function) - is when over-developed muscles on one side of the spine cause individual vertebrae to rotate and lose proper function. When muscle function declines muscles that support the spine respond in different ways, the spine can weaken or even atrophy.
- Histiopathology (Abnormal soft tissue function) - inflammation and swelling due to injured disc accompany the accumulation of blood and lymph - causing a rise in temperature.
- Pathophysiology - when there is a trauma to a joint, one of the ways your body responds is the stabilization of the area by forming new bone! With time, calcium deposits build up, eventually as abnormal bony growth. This arthritic 'splinting' of bones is nature's attempt to stabilize the injured joint.
Due to the intricacies of the nervous system, more research is being conducted in the areas of hormonal involvement, aging, immune system response, even genetic consequences. The Vertebral Subluxation Complex (pathomechanics of the spine)may be one of the most regular, yet overlooked sources of health problems.
Chiropractors are trained in identifying and treating vertebral subluxations/pathomechanics. This is done through first, the case history. A detailed case history often reveals the source of an underlying problem and barring the bizarre, the treating doctor can often make an accurate differential diagnosis from just listening to the patient. This is followed by the actual physical exam. X-Rays may be taken if indicated. Palpation (touching) the spine is also part of the exam and is utilized to locate pathomechanics. Provided the patient is accepted for care, and after a report of findings is made to the patient explaining everything the chiropractor will usually begin a series of chiropractic adjustments specifically designed to correct the vertebral subluxations/pathomechanics in your spine.
Chiropractors are the only professionals who undergo years of training
to be the experts at correcting subluxations/pathomechanics. While
Osteopaths (D.O.) have training in spinal manipulation, it is
chiropractors who have the more extensive training and perform over 95%
of the spinal manipulations in the USA. it is also chiropractors that
are publishing the most literature and the most widely read books on
aspects of chiropractic case management. Go to Amazon.com to find out
more regarding the two biggest health care books in Lippincott's
history:
Essentials
of Skeletal Radiology, Yokum & Rowe.
Whiplash Injuries: The
acceleration/deceleration syndrome, Foreman & Croft.
Yokum, Rowe, Foreman and Croft are all chiropractors.